
FAQ
Asbestos is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic " fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere by abrasion and other processes.
Colour: Green, Red, Yellow, White, Grey, Blue
Asbestos is dangerous because it causes cancer and pulmonary diseases. Long-term exposure creates a risk of mesothelioma, lung, laryngeal and ovarian cancer. Some people develop asbestosis, which involves progressive scarring of lung tissue. These conditions usually develop decades after exposure first began.
Friable – asbestos that is easily crushed into a powder. Friable asbestos has a higher risk of airborne fibres being released when it is handled. non-friable (bonded) – asbestos that is mixed with cement or resin to keep fibres in place. Non-friable asbestos poses a risk of releasing airborne fibres if it gets damaged.
Non-friable asbestos is a lower risk. It is mixed with cement or other hard bonding materials.
Non-friable asbestos can become friable if damaged or old. Non-friable asbestos material when dry cannot be crumbled, pulverised, or reduced to powder by hand pressure. It is also known as bonded asbestos.
A licensed asbestos assessor can confirm asbestos by inspecting the material and confirming with an accredited asbestos testing lab.
Below are some examples of Asbestos:
FRIABLE

NON-FRIABLE
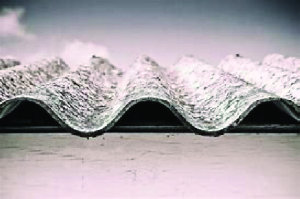
Any Buildings constructed prior to 1990 will most likely contain the product ASBESTOS.
Before commencing any Renovations or Building works it is in your own BEST interest to have it assessed by a Licensed Asbestos Assessor and have the product tested when necessary.
Our Capabilities